Tandem accelerator of ions
Ion sources
The laboratory is equipped with an Alphatross ion source (radio frequency plasma source producing ions from gases), and with MC- SNICS source (MultiCathode Source of Negative Ions by Cesium Sputtering) having a wheel accommodating up to 40 solid targets. The Alphatross is capable of creating a variety of negative ions. A positive ion beam is extracted from plasma produced in the radio-frequency (RF) source, and accelerated into the charge exchange cell at 6 keV where a portion (1–2%) of the beam is converted to negative ions, which are subsequently extracted and accelerated to the requested energy. Rubidium vapour is used in the charge exchange cell because of its high cross section for He- production. All elements, which can exist in gaseous form and can form negative ions (either atomic or molecular) could be considered candidates for ion production in the Alphatross ion source. The MC-SNICS ion source is used for production of ions from solid targets from lithium to transuranics. Typical currents obtained with carbon ions are around 100 μA.
Ion injection system
After the production and extraction of the ion beams from the Alphatross and MC-SNICS sources, the first E/q separation is made by an electrostatic analyser (ESA) with 300 mm radius of electrodes, mounted on a rotatable platform, so that ion beams from both ion sources can be chosen for further analysis. The X–Y steerers and slits can be used for beam tuning, attenuation and analysis before entering the injection magnet. The momentum analysis ME/q2, and separation of ions before acceleration is made by double focusing 90° magnet with bending radius of 0.4572 m, which is sufficient to analyse ions up to mass 333 amu at an energy of 40 keV from the ion source. After the proper mass is selected, a set of slits is used for parameterization of the beam, and a Faraday cup is used for measurements of ion currents. Negative ion beams produced in Alphatross or MC-SNICS ion sources, pre-accelerated to modest energies (40–100 keV) are then injected into the tandem accelerator.
Pelletron accelerator
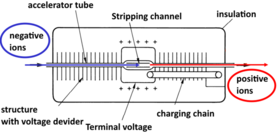
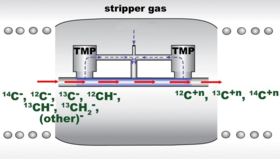
The NEC Model 9SDH-2 Pelletron, a 3 MV tandem electrostatic accelerator is capable of accelerating a variety of ion species over a broad range of energies for use in IBA, IBM, nuclear physics, and AMS studies. The 9SDH-2 terminal is provided with a gas (presently nitrogen) stripping system. Charging of the terminal is accomplished by a pellet chain (from which the name ‘‘Pelletron’’ is derived), made of metallic cylinders, joined by insulating links. The accelerator is housed in a pressure vessel (diameter of 1.22 m and length of 5.64 m), which allows an evacuation and subsequent filling with sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) insulating gas required for high voltage operation. A cryogenic-vacuum/pressure apparatus used for the evacuation, transport and storage of SF6 gas has been supplied by the DILO company (Germany).
Analyzers of accelerated ions
The accelerated ions are focused in the high-energy beam line with a magnetic quadrupole triplet lens, and a Y-axis electrostatic steerer. The quadrupole magnet is primarily used for IBA and NRA applications. The electrostatic quadrupole triplet lens used for AMS is installed inside the Pelletron pressure vessel. The switching magnet, presently also used as an analysing magnet (ME/Z2 = 300 amu-MeV @ ± 15°), is equipped with seven ports at ±45°, ±30°, ±15°, and 0° with respect to the accelerator. The beam lines from these ports will be used for IBA (channeling, RBS, PIXE, NRA, PIGE), IBM, nuclear reaction studies, nuclear microscope and for biomedical applications. The +45° and +15° beam lines are currently equipped with slits to control the divergence of the ion beam, with X–Y electromagnetic steerers, with Faraday cups for current measurements and with beam profile monitors. An RBS/PIXE/PIGE end station is installed at the +15° port.
More detail information on the characteristics of the tandem accelerator with associated equipment can be found in already published papers (Povinec et al. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 342(2015)321-326, and 361(2015)87-94), as well as in more recent papers listed in CENTA.
Analyzer of high-energy ions
A target, prepared from the investigated sample, is placed in the ion source, from which a beam of studied ions is forwarded to the tandem accelerator, and then, after acceleration and focusing of the beam, the ions are analysed in the high-energy analyser, consisting of high resolution electromagnet (radius 1,27 m, M/ΔM=725), two 45o electrostatic analysers (radius 2,54 m, E/ΔE=700) and the ionisation chamber as the end-of-the-line detector.