PIXE analysis of thin rabbit brain samples
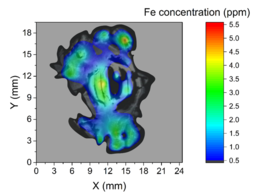
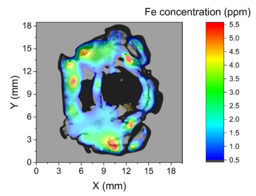
In cooperation with Medical faculties of the Comenius University in Bratislava and Martin a rabbit brain slice samples were received to determine iron concentrations and map its distribution in the specimen. The aim of this study was to evaluate concentrations of iron in these samples onvarious spots. It is expected that the iron in the rabbit brain was produced by electromagneticradiation similar to one generated in mobile telephones. The observed effects in the braintissue may be due to electromagnetic radiation, which causes agglomeration of iron in thetissue.
Proton beam (3 MeV energy, 300 pA intensity, 1.5 mm diameter) was used to analyze 4 samples:
- blank sample unexposed to electromagnetic (EM) radiation
- sample denoted as “First sample”, exposed to EM radiation. High Fe concentration (up to 50 ppm)
- 2 samples, RB01 and RB02 exposed to EM radiation. Low Fe concentration (up to 5.5 ppm)
A photograph of each sample was placed into the background of the Fe concentration maps. Dimensions of samples in millimeters are shown in the graphs. Fe concentration scale is different for the “First sample” because of much higher values compared to the other 3 samples.