Neutrinoless double beta-decay
Although neutrinos are one of the most abundant particles in the universe they are often called the most elusive particles of the Standard Model of nuclear physics. They have no electric charge, have very small masses and interact only via the weak interaction and gravity. Much is still to be learned about the neutrinos: their mass-generation mechanism, absolute mass scale, CP-transformation properties, and the question of whether they are Majorana fermions - i.e. identical to its own antiparticle, unlike all the other fermions of the Standard Model that are Dirac particles which have their distinct anti-particle partners.
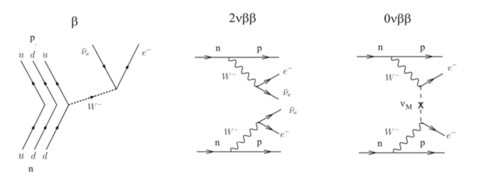
Experiments which can answer questions regarding their mass are searching for neutrinoless double beta-decay(0νββ). In fact, this decay is the only practical way to learn whether the neutrino is a Majorana or a Dirac particle. In this process, two neutrons are simultaneously transformed into two protons, emitting only two electrons – thus, violating lepton number conservation.
Feynman diagrams of beta-decay, double beta-decay and neutrinoless double beta-decay.
The experimental search for this decay is extremely challenging, with the best current half-life limits of >1026 yr. The necessary low radiation environment needed to search for such rare nuclear processes is provided by deep underground laboratories.
SuperNEMO
(Super Neutrino Ettore Majorana Observatory)
SuperNEMO is a modern neutrinoless double beta decay experiment currently being built in the Modane underground laboratory in France. SuperNEMO detector consists of a source foil of double beta emitter 82Se (but other candidates, such as 150Nd and 48Ca, are also possible) placed between 2 tracker volumes and 2 calorimeter walls made of plastic scintillator blocks with photo-multiplier tubes. This tracker + calorimeter design along with applied magnetic field allows for a reconstruction of charged particle tracks and energy measurements. Another important feature of SuperNEMO is the fact that the isotope source is separate from the detector, allowing several different isotopes to be placed between two trackers and to be studied. The whole experiment is conceived as 20 such identical planar modules, each containing 5-7 kg of ββ isotope, with the first module being called Demonstrator. The experimental signature of 0νββ are two electrons originating in the same location with their energy equal to the Q value of the decay with a daughter nucleus in a final state.
LEGEND
(Large Enriched Germanium Experiment for Neutrinoless Double-Beta Decay)
LEGEND is a next-generation germanium-based experiment to search for neutrinoless double beta decay. Building on success of previous generation experiments GERDA and MAJORANA, the LEGEND pursues a tonne scale of 76Ge. Phase of the experiment called LEGEND-1000 plans the exposure of 10 t.yr by operating 1000 kg of detectors for 10 years. So far, an initial baseline design has been established with bare germanium detectors operating in liquid argon.